


Alternote offers some standard text formatting features as well as the ability to read in a distraction-free environment.
Alternote tables free#
The app comes free of charge and features a lightweight and elegant interface that is intuitive.
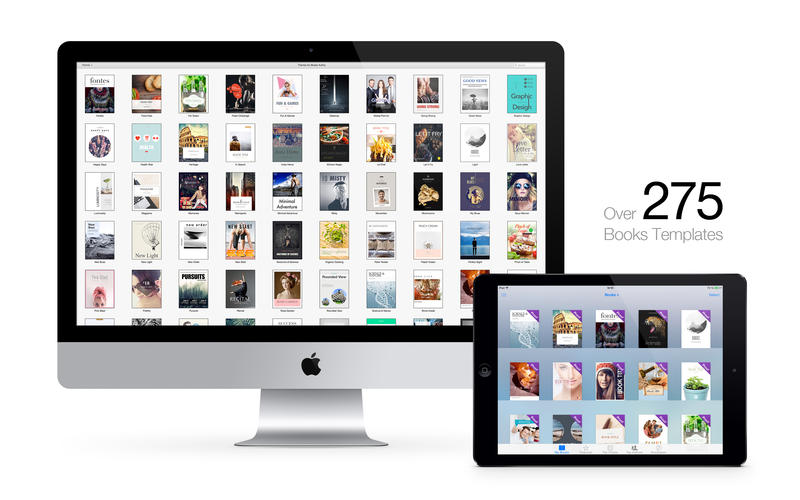
Alternote tables for mac#
For instance, the primary attributes for street address include prefix direction, prefix type, street name, street type, and suffix direction, and the same attributes are used for the alternate names in the alternate name table.Alternote for Mac connects to your Evernote account to enable you to access and interact with your notes. Records that are associated with Redlands have aĭepending on the locator role you choose and the type of features you want to search, attributes in the alternate name table are similar values that are found in the primary feature class. Primary city name and has a join ID value of 1, each correspondingĪlternate name also has the join ID value of 1. Value for all alternate names for that city. For example,Įach unique city for a Point Address locator must have one join ID Many-to-many or many-to-one relationship between the primary dataĪnd the alternate name in the alternate name table. Unique record in the alternate name table. Primary reference data role must contain a value that will beĪssociated with many records in the primary reference data and a Link primary features to alternate name table records when buildingĪ locator with the tool. Performance as well as geocoding quality.įields such as ObjectID, GUID, or GlobalID are not recommend for use as a join ID field to Using the ObjectID can increase the size of the locator and reduce batch geocoding The primary feature class must have a field that contains a unique ID value for each record that can be used to link to the Join ID from the alternate name table.ĭo not map the ObjectID in the primary reference data and alternate name table to the Join ID locator role field when building the locator. If the alternate name table contains multiple names for a single feature, the JoinID field will contain the same value for each alternate feature name record in the alternate name table. The alternate name table must have an ID field that can be used to join the records to the primary feature class. Additional names can be added to the table. Each record represents one name for a feature. The alternate name table contains fields for the additional names. Searching for a feature by all of its possible names can increase the success rate of geocoding. For example, North Park is a neighborhood Versus a commonly used name in which either could be used when You may have a neighborhood in a city or an official city name For example, Jefferson Road isĪ new official name for the street that was previously called Old Country Road. Names of features, such as streets, can change over time. Using this locator, you can geocode locations based on the name specified in the primary feature class or the alternate name table. To geocode these locations, a locator can be created using an alternate name table containing alternate street names for the primary features. In these instances, you may find that your address data refers to the same location by using a variety of alternate names.Īlternate name tables can be used for all of the supported locator roles and support alternate names for the features in the primary reference data. Street names and city names can change over time. For example, a highway might be known by a street name as well as a particular highway number. Sometimes features such as streets, cities, or places in primary address data are referenced by more than one name.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
